|

Home

Measurement
Setup

Dual-Stack
List

Connectivity

Hop
Count

RTT

Throughput

OS Dependence

IPv6 Address
Provisioning

IPv6 Tunnel
Performance

Scripts

References

Internal
Access 
|
|
Throughput
In this test, we used wget and wget6 to download
files from the dual-stack servers, and then analyzed the average download
throughput. In order to have an unbiased analysis, we downloaded files from
servers using different operating systems so as not to be influenced by the
type of Oses used by the servers. The files we downloaded have various
sizes ranging from 254KB to 538MB. In this test, we categorized our results
based on the downloaded file size, i.e. below 1MB (small), from 1MB to 10MB
(medium), from 10MB to 100MB (large) and above 100MB (enormous).
Figs. 6 and 7 show that IPv6 throughput is higher
than IPv4 throughput, especially for large and enormous download file sizes.
The average IPv6 throughput is 107.75KB/s, while the average IPv4
throughput is 77.88KB/s. This can be explained by the fact that the IPv6
backbone network is less congested compared to the IPv4 backbone network,
and as such, the IPv6 downloading rate is higher than that of IPv4.
Concentrating on the major cluster of points in Fig. 6, we see that the
IPv6 throughput for enormous-sized files is about 200KB/s; for the
large-sized files, the IPv6 throughput is about 100KB/s; for the
medium-sized files, the IPv6 throughput is about 150KB/s; and for the
small-sized files, the IPv6 throughput ranges from 50 to 100KB/s. These
results indicate that the bigger the file size, the higher the IPv6
throughput.
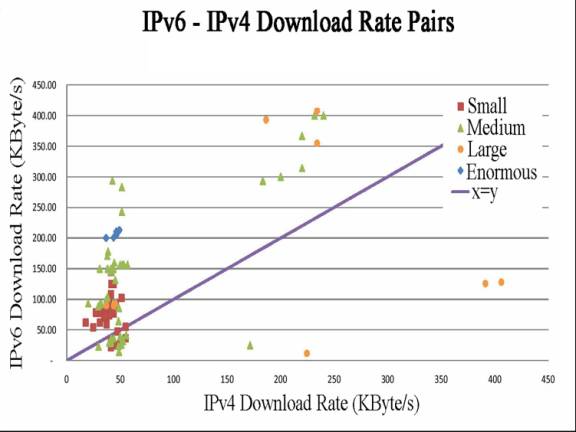
Fig.
6. IPv6-IPv4 Throughput Results
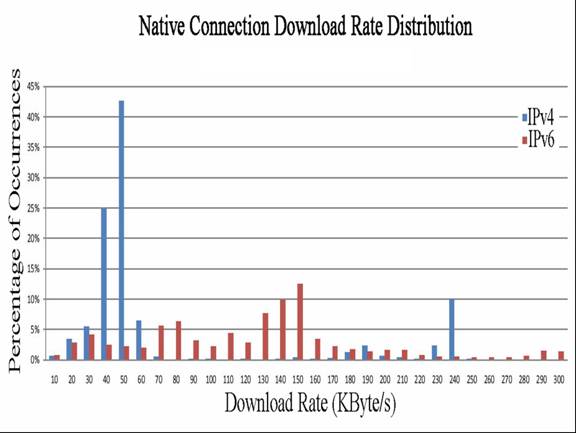
Fig.
7. Distribution of the IPv6-IPv4 Throughput Results
|
|